How Do Chatbots Work? Exploring the Technology Behind Conversations
Home » How Do Chatbots Work? Exploring the Technology Behind Conversations
- Oksana Chyketa
Key takeaways
- Chatbots are software programs that simulate human conversation to streamline customer communication, support, and lead generation.
- The main types of chatbots are rule-based bots, AI-based chatbots, and advanced AI agents that combine generative AI with backend integration.
- The pros and limitations of AI chatbots for businesses include instant support, efficiency, and scalability on the positive side, but challenges like security risks, integration hurdles, and long setup times remain.
- The key technology powering AI chatbots involves NLP, NLU, NLG, ML, RL, neural networks, and AI working together to understand language, detect intent, and generate responses.
- The anatomy of a chatbot consists of a user interface, NLP engine, dialogue manager, ML models, NLG engine, knowledge base, backend integrations, and a Q&A system.
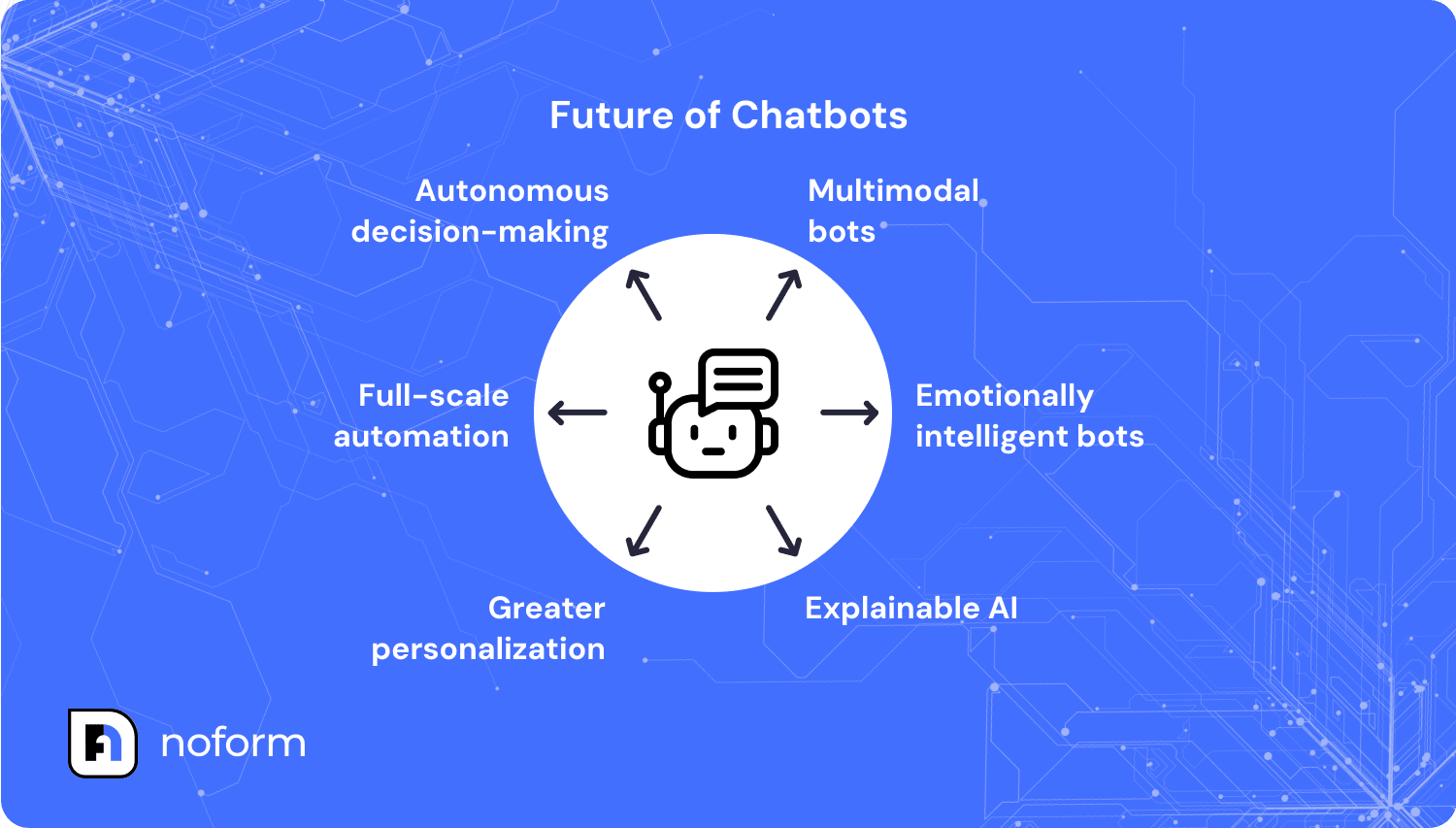
- In the coming years, chatbots will evolve with multimodal capabilities, emotional intelligence, explainable AI, deeper personalization, full-scale automation, and autonomous decision-making.
If you’ve opened a chat window on a website to ask about the return policy, looked up store hours, or gotten a quick link to schedule a call, you’ve probably interacted with a chatbot. Most people have—and often without realizing it.
For businesses, the shift has been dramatic. What used to feel experimental is now essential. Chatbots handle support at scale, qualify leads, and keep customers engaged around the clock. Their ability to simulate human conversation makes them a reliable extension of customer-facing teams. No surprise then that a Facebook survey found more than half of buyers prefer companies with chat-enabled support.
So, what is a chatbot and how does it work? More importantly, how do chatbots work in practice to deliver measurable results for businesses? This article takes you through everything—from their early history to the technologies driving them today, their strengths and shortcomings, and where the future is heading.
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate human conversation. Instead of clicking through menus or filling out long forms, you type a question, and the bot replies in natural language.
Think of an AI chatbot on a website that pops up in the corner of your screen when you’re browsing. You might ask it about shipping times, refund policies, or product details, and it instantly responds with the information you need.
The main purpose of a chatbot is to make communication faster, easier, and more consistent, especially in business contexts where customers expect immediate answers.
Today’s most advanced chatbots use conversational AI, which allows them to understand context, pick up on intent, and even detect nuances in human language.
But bots didn’t always look or act this way.
To understand how far the technology has come, it helps to take a step back.
Evolution of chatbots: Chatbots through the years
It’s tempting to think chatbots appeared out of nowhere in the last decade. In reality, the concept stretches back to the 1960s.
While early versions were primitive compared to AI-powered chatbots today, the underlying idea was the same: to enable human-like dialogue between people and machines. Each generation of bots brought new levels of sophistication, slowly shaping the chatbot technology we rely on now.
Legacy chatbots
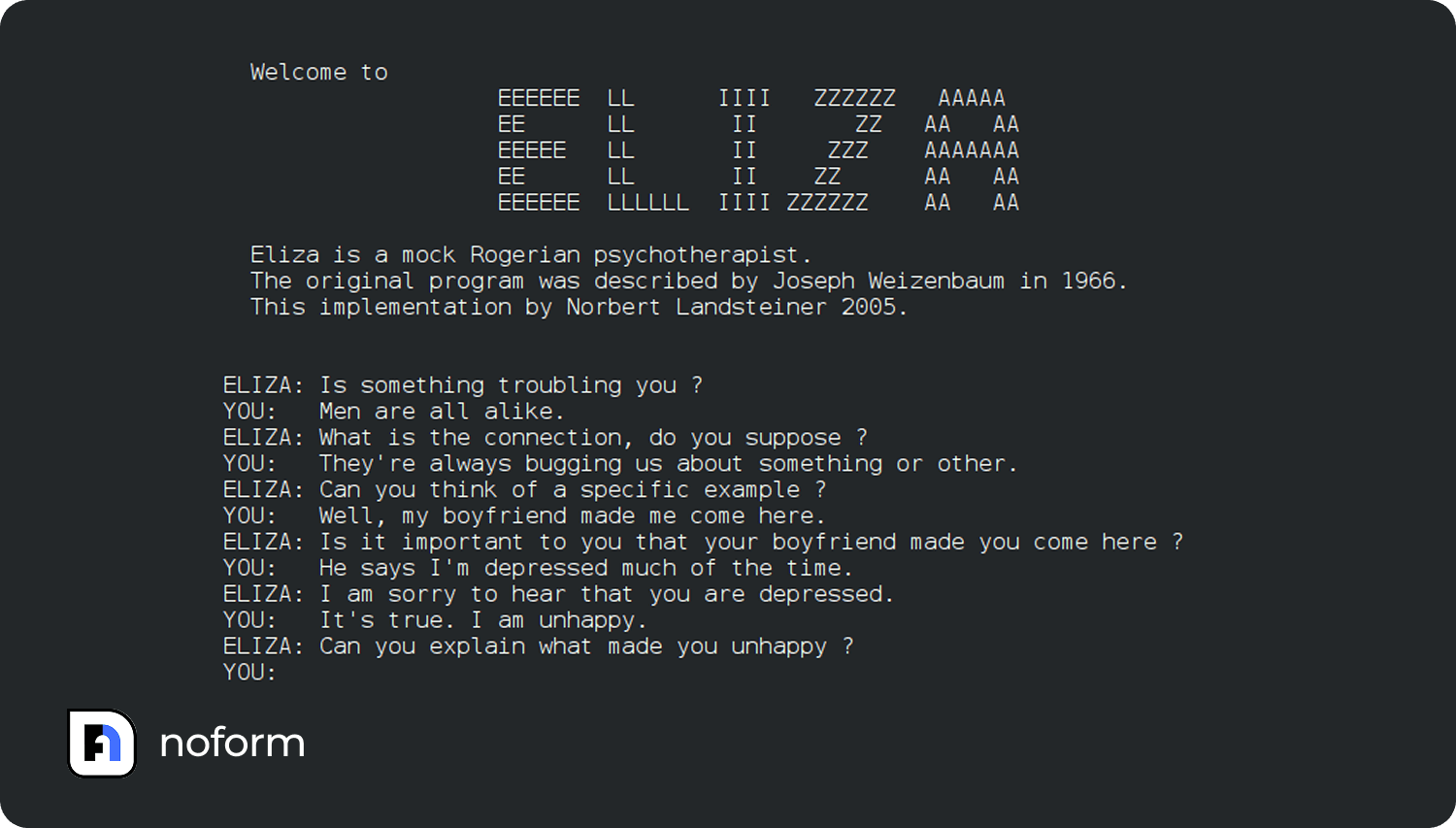
The first known chatbot, ELIZA, was created by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum in the 1960s. ELIZA mimicked a psychotherapist by turning user input into scripted replies. If you typed something like “I feel sad,” ELIZA might respond with “Why do you feel sad?” The illusion of conversation was there, but it relied entirely on keywords and phrases, not real understanding.
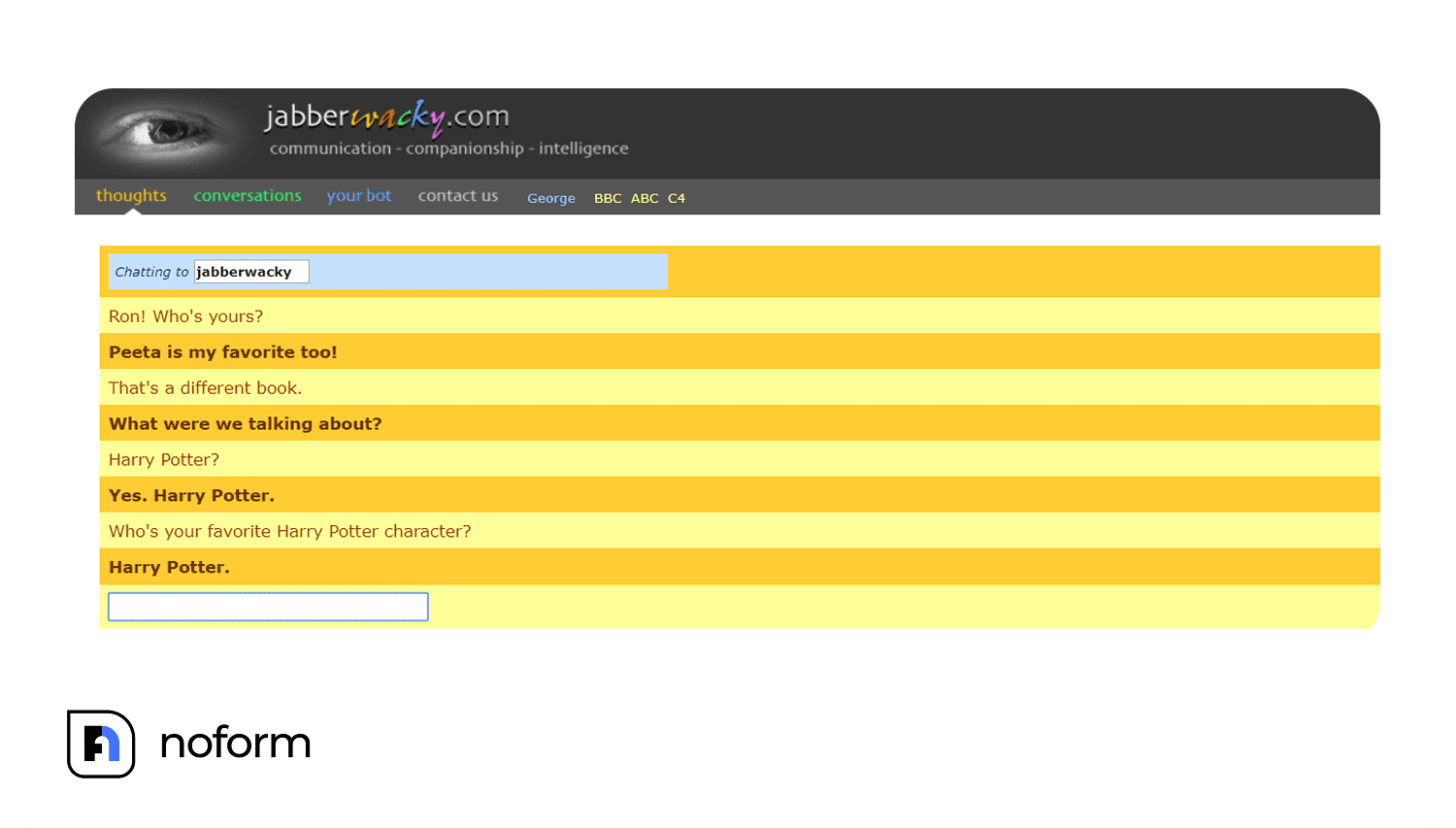
From the late 1980s through the early 2000s, entertainment-focused projects like Jabberwacky pushed the boundaries further. It used ‘contextual pattern matching’ to learn from past interaction snippets and keep conversations going.
Still, these traditional chatbots were limited, rule-bound, and often frustrating when users strayed outside expected inputs.
Key traits of legacy bots:
- Scripted responses only
- Triggered by keywords
- No real context awareness
- Minimal flexibility
They laid the groundwork but weren’t exactly conversational partners.
2010s rule-based bots
Fast forward to the 2010s and rule-based bots went mainstream. Voice assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa became household names. These virtual agents could set alarms, answer weather questions, or play music—but only if you asked in a way their coding recognized.
This era made chatbots widely accessible, but it also revealed their weaknesses. Anyone who’s ever shouted at Siri after being misunderstood knows the pain. Rule-based bots were rigid: stray from their programmed workflow, and they either failed or redirected you.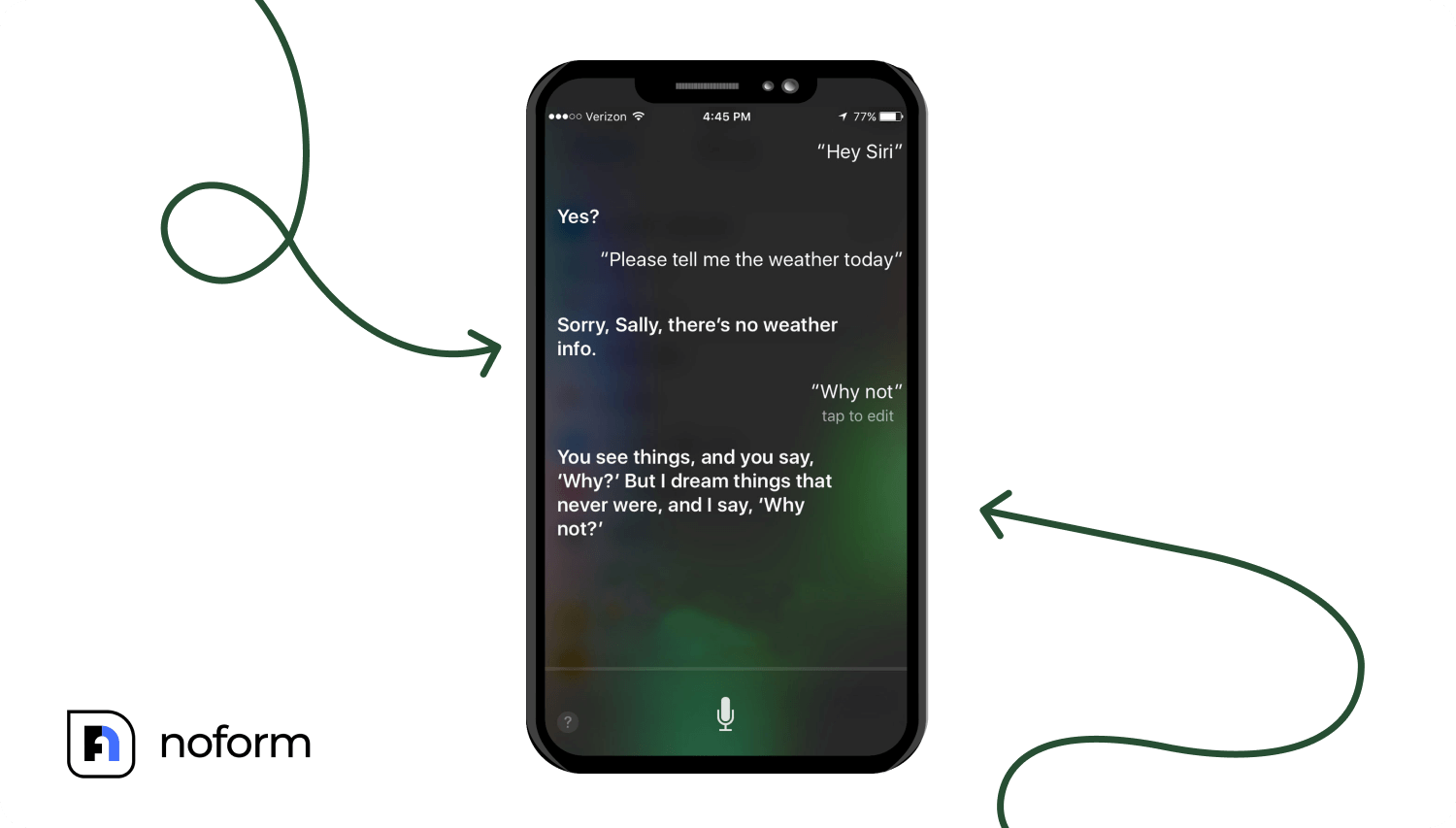
These bots showed the business world what chat automation could look like, but they weren’t yet ready to carry full customer service loads.
Modern AI-powered chatbots
The real transformation came with the rise of generative AI chatbots. Powered by large language models (LLMs), neural networks, and techniques like natural language generation, modern bots don’t just match keywords—they understand context, detect intent, and generate nuanced replies.
The turning point was OpenAI’s release of ChatGPT in late 2022. Suddenly, conversational bots weren’t a novelty but headline news. This new wave of AI-powered chatbots could handle complex dialogues, draft emails, answer multi-step questions, and even initiate backend workflows like scheduling or pulling customer data.
Other players, like DeepSeek and Google’s Gemini, pushed the envelope further, cementing AI chatbot software as enterprise-grade tools.
For businesses, the difference is night and day. Modern bots can:
- Provide 24/7 customer support across channels
- Learn from past interaction history
- Personalize customer experience in real time
- Integrate with CRMs, helpdesks, and workflow automation
What started as scripted keyword-matching in the 1960s has now become a flexible, adaptable AI agent that can scale support, boost efficiency, and meet rising customer expectations.
What are the main types of chatbots?
The evolution of chatbot technology isn’t just about how conversations feel. The real distinction between traditional chatbots and today’s AI-powered chatbots lies in the underlying technology.
Some are powered by simple scripts and structured data, while others use artificial intelligence and deep learning to adapt on the fly.
These differences give us three different types of chatbots, each suited to different business needs.
Rule-based chatbots
Rule-based chatbots are the simplest form. They follow a predefined set of instructions, usually built around decision trees, keyword detection, and pre-written templates. When a user types something that matches the bot’s rules, it serves up the scripted reply.
They shine in predictable scenarios like FAQs (learn more about FAQ chatbots in our guide), appointment scheduling, or structured forms where the flow doesn’t change much.

But they can’t adapt beyond their script, they don’t improve over time, and if the user strays outside the rules, the conversation often breaks.
AI-based chatbots
AI-based chatbots take things further by relying on natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and natural language generation (NLG). Instead of simply matching keywords, they analyze what’s being said and why. The process typically involves:
- Breaking down user input (tokenization) into smaller pieces of data
- Classifying intent to understand what the person wants
- Recognizing entities like names, dates, or product references
This allows them to handle more complex, dynamic, and personalized conversations.
For businesses, the benefit is clear: AI-powered chatbots can help process a significant volume of customer inquiries without relying on rigid scripts.
The drawback is that they need training data, thoughtful design, and continuous updates to stay accurate and avoid misinterpretations.
AI agents
The newest stage in this evolution is the rise of AI agents, the next generation of virtual agents. They combine generative AI with principles of conversation design, trained on vast datasets of interactions, and use deep learning to recognize context, adapt responses in real time, and integrate with backend platforms for tasks like updating CRMs or processing refunds.
Unlike earlier bots, AI agents aim for end-to-end resolution—they answer and act. Their power lies in enterprise-scale automation, though this comes with higher implementation costs and the need for strict oversight on accuracy and security.
When should you use an AI chatbot?
An AI chatbot is most effective for companies managing high volumes of data and customer conversations. In these environments, users phrase the same requests in many different ways, and artificial intelligence is far better at interpreting that variety than manually scripting every reply.
Customer support
Modern customer service bots excel in handling repetitive questions while keeping tone and accuracy consistent. They adapt to varied speech patterns and deliver automated responses that resolve issues quickly.
With the right chatbot features, businesses can improve customer communication, reduce wait times, and let human agents focus on more complex cases.
Lead generation
A customer acquisition chatbot engages visitors 24/7, collects details, and qualifies prospects without human intervention. Instead of relying on static forms, companies can use chatbots to qualify leads by asking targeted questions, capturing intent, and routing opportunities to the right sales team. This is where chatbots automate one of the most time-consuming parts of the funnel.
Industry-specific solutions
AI chatbots are adaptable across industries, delivering speed and reliability in different contexts:
- Insurance chatbots streamline claims and policy inquiries
- AI banking chatbots process balances, payments, and fraud alerts
- AI chatbots for ecommerce manage orders, returns, and recommendations
- Healthcare AI chatbots assist with scheduling, patient intake, and symptom checks
- AI solutions for car dealerships book test drives, guide shoppers, and answer inventory questions
- AI chatbots for roofing companies handle quotes, appointments, and service inquiries
- AI for pet services answer common pet questions, manage grooming and vet bookings
- Real estate AI assistant qualifies leads, answers property questions, and schedules showings
The bottom line is, when organizations face significant volumes of repetitive requests—or when customers expect instant answers—chatbots provide a scalable way to deliver. By combining conversational interfaces with robotic process automation, they ensure speed, accuracy, and always-available service. For companies aiming to boost efficiency without sacrificing the customer experience, AI chatbots are now essential.
How do chatbots work (step by step)?
At a high level, the process looks straightforward: a user asks a question, the chatbot figures out what that question means, and then it responds. But under the hood, several steps happen in rapid sequence to make the interaction feel natural. Understanding these steps is key to answering “how does chatbot work” and, more specifically, “how do AI chatbots work.”
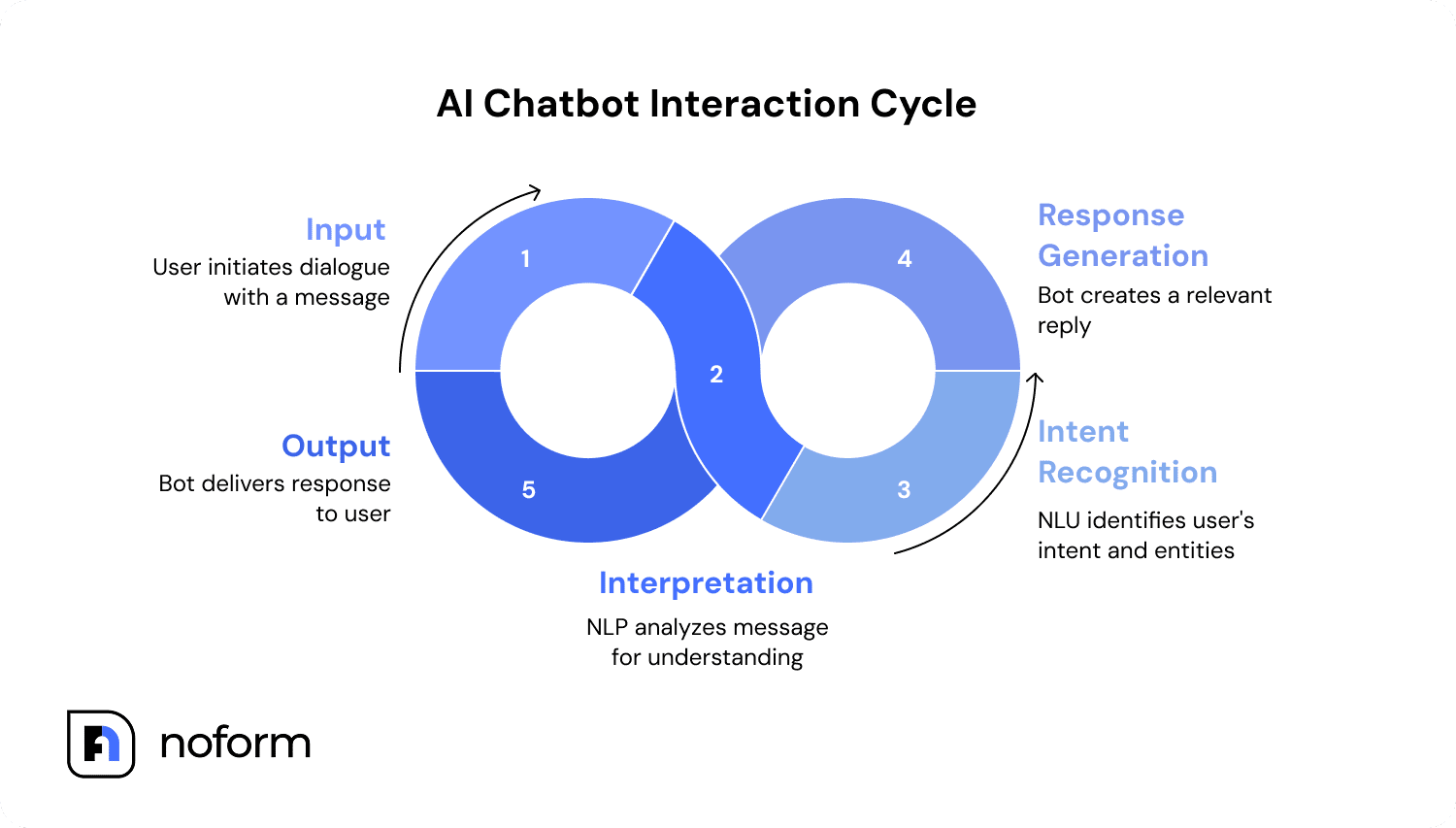
Step 1: Input
The cycle begins when a user types a message. For example, someone might type, “What’s your return policy?” into a website AI chatbot. This input kicks off the entire process.
Step 2: Interpretation
The chatbot’s natural language processing (NLP) engine breaks down the raw text. It looks at grammar, syntax, and context to make the input understandable to the system. If the user asks, “Can I send this back if it doesn’t fit?” NLP interprets this as a question about returns even though the word “return” wasn’t used.
Step 3: Intent recognition
Once the text is processed, natural language understanding (NLU) takes over. Here, the system identifies what the user actually wants (the intent) and spots any specific details (the entities). This is where named entity recognition comes in—for example, detecting product names, dates, or numbers within the request.
Step 4: Response generation
At this stage, the bot decides how to reply. Depending on its setup, it might:
- Pull information from a knowledge base or backend system (for example, accessing an order database to check delivery status)
- Use pre-programmed replies designed for common questions
- Rely on knowledge models to generate a more flexible response if it’s an AI-powered system
This is the step where access to business systems makes a big difference. A support bot tied to inventory or shipping software can provide real-time updates instead of generic answers.
Step 5: Output
Finally, natural language generation (NLG) turns the decision into a human-like message and delivers it back to the user. The customer reads: “You can return items within 30 days as long as they’re in original condition.”
The process doesn’t stop there. Each reply closes one loop of the cycle, but the exchange continues until the query is fully resolved. That’s the foundation of how AI chatbots work: rapid, repeated cycles of input, interpretation, recognition, generation, and output, all designed to keep the dialogue flowing naturally.
Key technologies that power chatbots
In the previous section, we broke down how AI chatbots work step by step. Behind each of those steps sits a set of technologies that make the process possible. These tools work together to understand language, detect intent, generate answers, and refine performance over time.
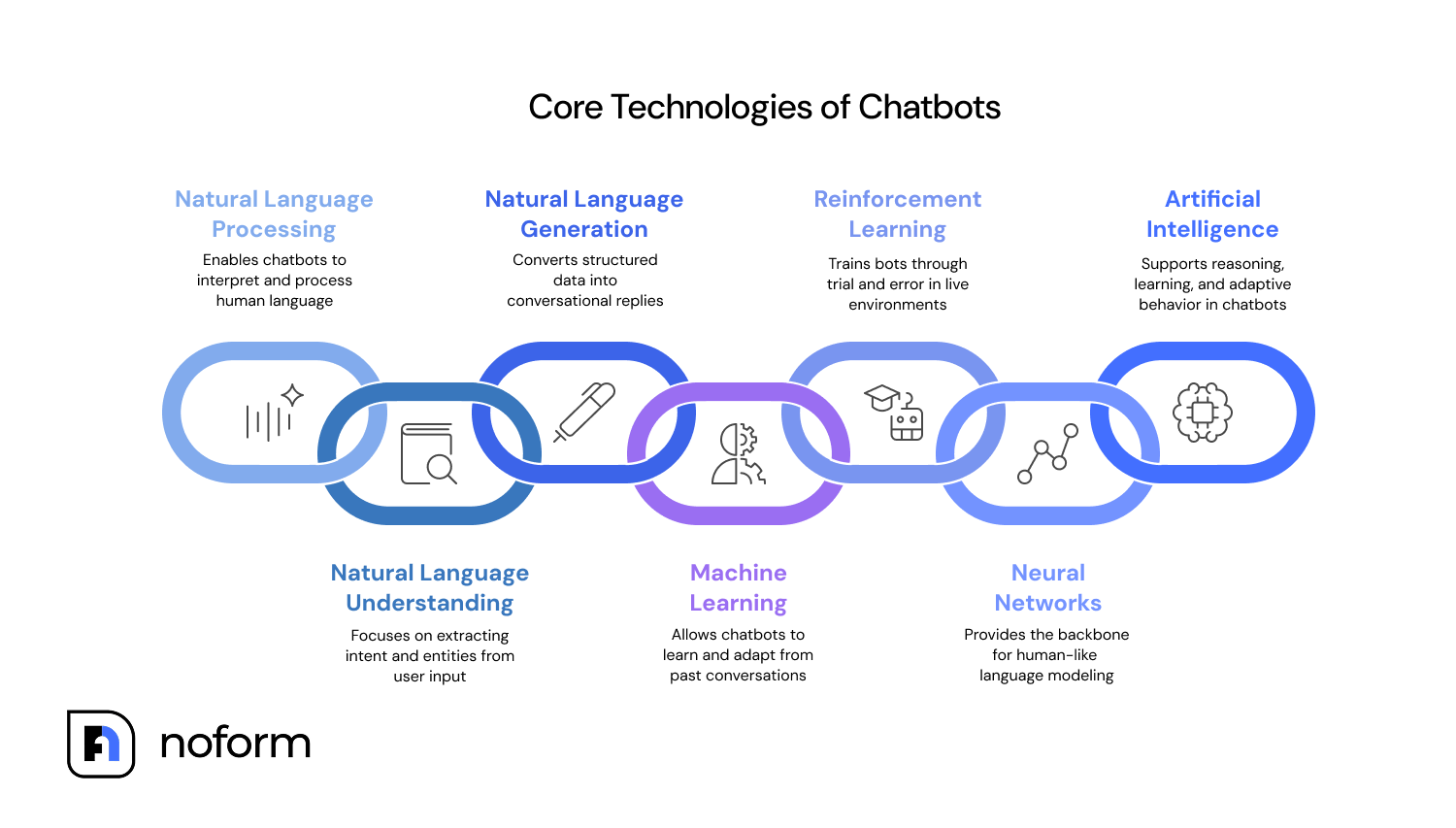
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – The engine that enables chatbots to interpret and process human language, whether typed or spoken.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU) – Focuses on breaking down user input and extracting both intent and entities, such as names, numbers, or dates.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG) – Converts structured data or decisions into clear, conversational replies that sound natural to the user.
- Machine Learning (ML) – Allows chatbots to learn from past conversations, adapt to new phrasing, and improve accuracy with ongoing use.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) – Trains bots through trial and error in live environments, rewarding successful outcomes and reducing mistakes over time.
- Neural Networks – Provide the backbone for human-like language modeling by recognizing patterns in massive datasets and powering large language models.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) – The overarching layer that supports reasoning, learning, and adaptive behavior, enabling chatbots to simulate human-like communication and handle complex queries.
Together, these technologies form the foundation of modern chatbot technology, turning simple question-and-answer scripts into systems that can scale, learn, and adapt across industries.
Chatbot architecture explained
The technologies we covered earlier—NLP, ML, neural networks—come together inside a chatbot’s architecture. Each layer has a specific role in turning input into a smooth conversation.
- User Interface (UI) – The front end where people interact, whether through a website chat window, app, or voice assistant.
- NLP Engine – Processes and interprets messages so the system understands user language.
- Dialogue Manager – Maintains context and keeps replies consistent across turns.
- Machine Learning (ML) Models – Learn from interactions to improve accuracy and adapt to new phrasing.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG) Engine – Converts structured data into human-like replies.
- Knowledge Base / Database – Stores FAQs, product details, and user data for quick retrieval.
- Backend Integrations – Connect to CRMs, order systems, or ticketing tools to pull or update live information.
- Q&A System – Delivers instant answers to common questions using manual or auto-trained content.
Together, these components allow a chatbot to interpret, respond, and refine conversations at scale.
Limitations and challenges
So far, we’ve focused on what chatbots do well. To fully understand how chatbots work, though, it’s important to recognize their limits.
Handling sensitive data such as payments or medical records introduces security risks, so compliance with GDPR, encryption, and strict access controls is essential. Even enterprise-grade chatbots can misinterpret slang or idioms, exposing gaps in natural language understanding that reduce accuracy and trust.
Integration is another hurdle. Many companies still rely on legacy systems that don’t connect smoothly with modern AI, making it difficult for bots to access CRMs or order data in real time. Consistency across channels also remains challenging, since customers expect the same user experience on websites, apps, and messaging platforms.
To bypass this bottleneck, NoForm provides ready-made integrations through Zapier and Make, allowing teams to connect chatbots seamlessly with a wide range of tools and systems without extensive custom development.
Global operations add complexity. Translation tools help, but cultural nuances are often lost, limiting the quality of multilingual support. Unless, of course, you don’t opt for chatbot software like NoForm—our multilingual features make it easier to deliver consistent, high-quality service across different languages and regions, reducing friction in global deployment.
Finally, creating chatbots use demands significant setup. From integration and data preparation to thorough testing chatbots before launch, implementation can stretch for weeks or even months.
But, of course, it doesn’t have to! With NoForm, setup is designed to be faster and lighter, so businesses can get their chatbots up and running with less overhead.
Future of chatbots: Current and emerging trends
The current moment is one of the most productive eras in chatbot development. Advances in artificial intelligence, deep learning, and large-scale deployment have moved the technology far beyond scripted replies. What we’re seeing now is only the beginning—several trends are set to redefine how businesses and customers interact:
- Multimodal bots: Future chatbots won’t be limited to text. They will combine voice, images, and text in one interface, allowing users to describe a product with a photo, ask a question out loud, and receive a written response instantly.
- Emotionally intelligent bots: Developers are working on systems that detect tone and sentiment, helping bots respond in a more empathetic way. This shift has the potential to improve trust and make digital interactions feel more human.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Transparency is becoming essential. Chatbots powered by XAI will be able to show how they reached a conclusion, helping businesses build confidence in automated decisions and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Greater personalization: With deeper profiling and smarter knowledge models, chatbots will deliver experiences tailored to each user. From product recommendations to individualized support, personalization will move from optional to expected.
- Full-scale automation: Analysts forecast that chatbots could eventually manage 80–100% of routine customer interactions. This would free human teams for strategy, complex problem-solving, and relationship-building.
- Autonomous decision-making: The most advanced AI agents will not just respond but also take workflow-level actions. From authorizing refunds to triggering supply chain updates, chatbots will become true participants in business operations rather than passive tools.
Businesses that adopt these innovations early stand to shape expectations while others are still catching up.
Summing up
A clear understanding of how chatbots work gives companies the confidence to select the right tools, connect them to existing systems, and expand their use as needs grow. What once felt experimental is now a core part of business strategy.
Chatbots deliver quick, personalized support, raise efficiency, and cut costs. They’ve become indispensable across the board—from small businesses aiming to streamline communication to enterprises deploying enterprise-grade chatbots at scale.
The next step is simple: see the impact for yourself. Book a demo call and try NoForm AI to discover how intelligent automation can reshape customer engagement in your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do chatbots work?
Chatbots work by processing user input through a cycle of interpretation and response generation. When a user sends a message, the chatbot uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to break down the text, Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to identify the user’s intent (e.g., schedule a property viewing), and Natural Language Generation (NLG) to construct a human-like reply based on data from its knowledge base.
What are the main types of chatbots?
There are three main types of chatbots used in business today:
- Rule-Based Chatbots: These rely on pre-scripted decision trees and keywords. They function like interactive FAQs and are best for simple, predictable tasks.
- AI-Based Chatbots: These use Machine Learning and NLP to understand context and intent, allowing them to handle dynamic conversations without rigid scripts.
- AI Agents: The most advanced type, these agents combine generative AI with backend integrations to perform autonomous tasks, such as updating a CRM or processing a refund.
What is the difference between NLP and NLU?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the broad technology that enables computers to read and process human language. Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is a specific subset of NLP that focuses on determining the meaning behind the text. While NLP parses the sentence structure, NLU deciphers the user’s intent (what they want) and extracts entities (specific details like dates or product names).
What are the benefits of using AI chatbots for business?
AI chatbots provide scalability and efficiency by automating customer support and lead generation. They offer 24/7 availability, eliminating wait times for customers, and can handle thousands of concurrent conversations. Additionally, they reduce operational costs by managing routine queries, freeing up human agents to focus on complex, high-value interactions.
Will chatbots replace human customer service agents?
No, chatbots are designed to augment, not replace, human teams. Experts predict that while chatbots will eventually automate 80–100% of routine interactions, their primary role is to handle repetitive tasks. This shift allows human agents to focus on strategy, empathy-driven relationship building, and solving complex problems that require critical thinking.